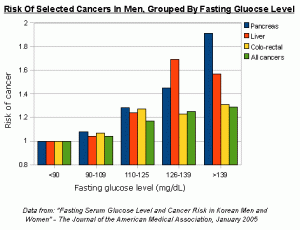
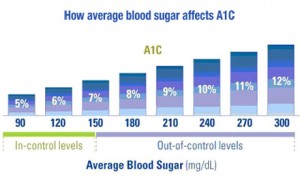
Normal Random Blood Sugar Levels
Normal random blood sugar levels fall within a standard range of between 70mg/dl to 150mg/dl. This variation can be attributed to various factors including the time, type, and volume of food consumed during previous meals.
When you eat foods that are high in carbohydrates, pancreatic secretions of glucagon and insulin regulate the glucose levels. However, the main problem arises when the pancreas does not secrete sufficient amounts of insulin to convert glucose into energy.
The condition of extremely high blood sugar is known as Hyperglycemia which can damage various organs resulting in kidney damage, nerve damage, loss of vision, and heart disease. The other extreme of low blood sugar is known as hypoglycemia and the patient might lose consciousness in case the blood sugar level is too low.
In case your blood sugar level does not fall within the normal range, appropriate action should be taken to diagnose the condition. Here are some tests to help diagnose diabetes and help diabetics ascertain how to manage the disease in the best way possible.
-
Random Blood Glucose Test
Normal random blood sugar levels
Random blood glucose tests are used to measure the amount of blood sugar or glucose circulating in your blood. Random blood sugar levels are used to determine whether you’re likely to have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes. However, other tests are usually necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
What is random blood sugar testing?
Random glucose tests measure the amount of blood glucose at any given time during the day. Many blood glucose tests involve either continuous or fasting monitoring, but a random blood sugar test does not. However, random tests are particularly useful for someone who needs a speedy diagnosis and medical attention. Moreover, random blood sugar testing is an essential tool for diabetics because it helps determine how well the condition is being managed.
Reasons for random testing
Diabetes is a condition that affects the body’s ability to produce, release or use insulin once sugar is converted to glucose. Therefore, your doctor might recommend a random blood sugar test if you’re showing symptoms of diabetes. Early signs and symptoms of diabetes include:
- Excessive thirst and urination
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Slow healing of cuts, bruises, and wounds
- Tingling in legs and arms (diabetic neuropathy as a result of uncontrolled diabetes)
Type 2 diabetes tends to develop slowly and symptoms can be hard to detect especially during the early stages.
Random glucose testing and diabetes management

- Experience stress
- Eat at different times of the day
- Vary their diet
However, if you have prediabetes or diabetes, your random blood sugar levels can vary significantly throughout the day, especially if the disease is not managed well.
Random blood sugar tests are performed outside the normal testing schedule. If you have normal random blood sugar levels, you may not be suffering from diabetes. However, as mentioned earlier, your doctor may recommend additional tests to confirm the diagnosis. On the other hand, if you have diabetes and your random blood sugar levels are within the acceptable range, your management plan is probably working.
Wide variations in your random blood sugar levels typically suggest the need to change your strategy. It is essential to ensure that your random blood sugar levels are within the normal or acceptable range to avoid the complications caused by consistently high blood sugar levels.
When to test
For people with diabetes, it’s very important to pay attention to the symptoms. If you’re experiencing any signs of low blood sugar, test immediately. Random blood sugar tests can help you detect hyperglycemia and reduce the risk of serious and potentially fatal complications.
If you have diabetes, testing your blood sugar levels at various different times over the course of the day is very important as it can help you manage your condition more effectively and lower the risk of serious diabetes complications.
If random glucose test results indicate that your blood glucose levels are higher than expected, the doctor usually orders follow-up tests to confirm the diagnosis. Follow-up diabetes tests usually include:
Fasting glucose test:
This blood sugar test measures the blood glucose level after staying for at least 8 hours without eating or drinking anything except water. The fasting blood sugar level for a healthy person ranges between 70 mg/dl and 100 mg/dl. If the fasting glucose level exceeds 125 mg/dl for two consecutive tests, the person might be suffering from diabetes. Fasting glucose tests are usually performed in the morning before you’ve had breakfast.
OGTT (Oral Glucose Tolerance Test):

If your doctor suspects that you have diabetes, they usually recommend an oral glucose tolerance test which also requires you not to drink or eat for at least 8 hours. After the doctor takes the first blood sample, you’ll drink a glucose solution and then the doctor will take more samples over the next 2 hours.
This test is usually used to evaluate the body’s response to sugar. The present blood sugar level is measured first after which a glucose solution (175 gm glucose) is given to the patient. After this, the blood glucose level should be measured at 30-minute intervals six times. For non-diabetics, the blood sugar level does not rise above 140 mg/dl at any time.
However, a blood glucose level of between 140 mg/dl and 199 mg/dl indicates that the person might be pre-diabetic. A blood glucose level of 200 mg/dl or more suggests that the person is suffering from full-blown diabetes. The main objective of a glucose tolerance test is to assess the reaction of your body to the sudden influx of glucose.
Glycated Hemoglobin Test:
Although the glycated hemoglobin test is not for the diagnosis of diabetic conditions, this test shows how well the patient has been managing diabetes for the past 3 months. These normal blood sugar levels should always be less than 7%. In case the level is above 7%, it is vital for the doctor to change your treatment plan.
Managing the blood glucose level (and maintaining normal blood sugar levels) is a vital aspect of controlling various diabetic conditions. Moreover, you can test your blood sugar from anywhere by simply using the correct equipment and paying attention to directions. You should also keep a good record of your test results in order to identify potential problems.
Interpreting random blood sugar test results.
The amount of glucose in your blood is measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Normal random blood sugar levels for a person without diabetes should be below 200 mg/dL.
According to one 2015 study, random glucose test results of over 100 mg/dL is a great risk factor for diabetes. A result of 200 mg/dl or more indicates that you may have diabetes. However, the doctor may repeat the random test on another day and recommend a different test for a reliable diagnosis.
 Help yourself to Maintain Normal Blood Sugar Levels!
Help yourself to Maintain Normal Blood Sugar Levels!
You know a lot of diseases can be managed and even reversed, by regular exercise, a good healthy eating plan, (monitored carefully by your health care professional), keeping well hydrated, and getting plenty of rest.

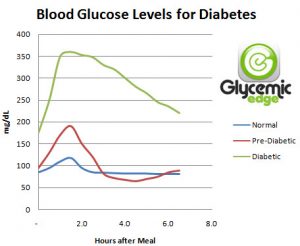


 Renal glycosuria is a rare condition that is typically caused by kidney damage. This condition occurs when a person’s kidneys are unable to reabsorb blood glucose despite the person having normal blood sugar levels.
Renal glycosuria is a rare condition that is typically caused by kidney damage. This condition occurs when a person’s kidneys are unable to reabsorb blood glucose despite the person having normal blood sugar levels.