What are Normal Hemoglobin A1C Levels?
Hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c levels indicate the average blood sugar level over 2 to 3 months. The A1c test, also known as glycosylated hemoglobin, glycated hemoglobin, glycohemoglobin or HbA1c test must be done in order to determine your hemoglobin A1c levels. T
his test is commonly used to diagnose diabetes and pre-diabetes, and it also helps you and your diabetes healthcare team create an effective diabetes management plan. Higher hemoglobin A1c levels are associated with diabetes-related complications. Therefore, it is essential to achieve and maintain your Hemoglobin A1c goals if you have diabetes or pre-diabetes.
People who have pre-diabetes or diabetes need the A1c test regularly to check whether their A1c levels are within range. It also tells your diabetes care team if your medications need to be adjusted.
What is the A1c test?
When glucose enters the bloodstream it bonds with hemoglobin, a type of protein the red blood cells. Although we all have sugar attached to our hemoglobin, if you have higher blood sugar levels, you have more sugar attached to your hemoglobin. Physicians use the A1c test to measure the percentage of red blood cells that have glucose-coated hemoglobin.
Testing for pre-diabetes and diabetes: Who should get tested and when?
Anyone over the age 45 should get a baseline A1c test. You should also go for the test if you are under 45 and have any risk factor for type 2 diabetes or pre-diabetes.
How often should you get tested?
- If your A1c levels are within the normal range and you have ever been diagnosed with gestational diabetes or have one or more risk factors repeat the test every 3years.
- If your A1c levels indicate that you have pre-diabetes, consult your physicians about the steps you can take to improve your health and minimize the risk for developing type 2 diabetes. Repeat the test as often as recommended, usually every year.
- If you’re not showing any symptoms but your A1c test results show you may have diabetes or pre-diabetes, confirm the results by getting tested on a different day.
- If your A1c test results show you have diabetes, work with your doctor to create the best diabetes healthcare team and join diabetes education and support groups so you can effectively manage your diabetes.
- People who have diabetes should get the test twice a year or more often if they have other health conditions or if your medication has been altered. Consult your doctor about how often you should get an A1c test.
Diagnosing Diabetes or Pre-diabetes
| Normal | Less than 5.7% |
| Pre-diabetes | 5.7% to 6.4% |
| Diabetes | 6.5% or more |
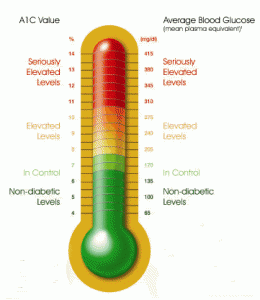
Normal A1c levels are typically below 5.7%, levels of between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate pre-diabetes, and levels above 6.5 indicate diabetes. If your A1c levels are within the pre-diabetes range, you have a greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
A1c test results can also be displayed as eAG (estimated average glucose), the same numbers displayed on most blood sugar meters (mg/dL).
| A1C | eAG mg/dL |
| 7% | 154 |
| 8% | 183 |
| 9% | 212 |
| 10% | 240 |
Factors that can affect A1c test results
Various factors can falsely decrease or increase your hemoglobin A1c levels, including:
- Conditions such as severe anemia, liver disease, and kidney failure.
- A rare kind of hemoglobin that people with certain conditions (such as thalassemia or sickle cell anemia) as well as people of Mediterranean, Southeast Asian, or African descent may have.
- Medications, including some HIV medications and opioids.
- Blood transfusion or blood loss
- Late or even early pregnancy.
You should let your physician know if one or more of these issues apply to you.
Your Hemoglobin A1c Goals
The goal for most diabetes patients is to maintain A1c levels of 7% or below. However, personal goals depend on several factors including other medical conditions and your age. Therefore, you should work with your diabetes healthcare team to set your own personal A1c goal.
For instance, your people with diabetes may have more years with the condition ahead. As a result, their A1c goal could be lower in a bid to reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. The goal may also be different for patients who frequently have hypoglycemia.
On the other hand, older folk, people who have severe lows (hypoglycemia) or other health complications may have a higher A1c goal.
Although the A1c test is an important test, it is extremely essential to keep in mind that A1c tests are not a substitute for daily blood sugar self-testing, particularly for people who have diabetes.

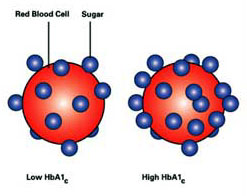

 Hemoglobin is a protein based, iron containing component in red blood cells that is primarily responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs and transferring it around the body to be used by the cells. Glucose also binds to some hemoglobin and stays bound to it for the length of the life of the red blood cells which is about 120 days.
Hemoglobin is a protein based, iron containing component in red blood cells that is primarily responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs and transferring it around the body to be used by the cells. Glucose also binds to some hemoglobin and stays bound to it for the length of the life of the red blood cells which is about 120 days.