What are Borderline Diabetes Symptoms?
Borderline diabetes, also known as pre-diabetes is a condition that typically develops before progressing to full-blown type 2 diabetes. Also known as glucose intolerance or impaired fasting glucose, it means that although you have higher than normal blood glucose levels, they are not high enough to be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes.
Overview
If you have borderline diabetes, the pancreas still produces adequate insulin in response to carbohydrates you’ve ingested. However, the amount of insulin produced is still less effective at getting rid of sugar from your bloodstream, so blood sugar levels remain higher than normal. This condition is commonly known as insulin resistance.
If you’ve been diagnosed with borderline diabetes, it’s important to understand that you are not alone. A 2015 study showed that 1 in 3 American adults had the condition. That’s about 84.1 million Americans.
Having borderline diabetes does not necessarily mean you’ll develop diabetes. It’s simply a warning of what could happen in the future. However, people with borderline diabetes have a significantly higher risk of being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes compared to people with normal blood glucose levels. The risk increases if they don’t make healthy lifestyle changes to their activity habits and diet.
What are the symptoms of borderline diabetes?
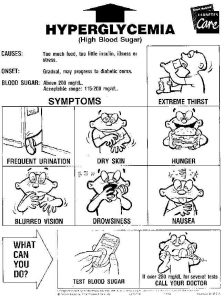
Borderline diabetes does not typically have any clear tell-tale signs or symptoms. However, one possible sign is darkened skin or some parts of the body such as the neck, knuckles, elbows, and knees.

- Excess hunger
- Blurred vision
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Increased thirst
When should you see a doctor?
It is extremely important to see a doctor if have any concerns about diabetes if you’ve noticed any signs or symptoms of type 2 diabetes or have any risk factors for the condition.
What are the causes of prediabetes?
Although the exact cause of borderline diabetes isn’t known, factors such as genetics and family history play a significant role. Other important factors include excess belly fat, being overweight, and failure to engage in regular physical activity.
However, it’s clear that people with borderline diabetes don’t process blood glucose properly anymore. This results in the accumulation of sugar in the bloodstream instead of being absorbed and used by cells in tissues for energy.
Glucose in our bodies comes from the food we eat. When food is ingested and digested, glucose enters the bloodstream. However, cells require a hormone known as insulin in order to absorb glucose from the bloodstream.
Insulin is produced by a gland called the pancreas which sends insulin to the bloodstream once the food is ingested. Insulin enables cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream, hence lowering the amount of glucose in the blood. When blood sugar levels start to drop, secretion of insulin into the bloodstream is gradually reduced.
For people with borderline diabetes, this process is impaired. Cells may become resistant to insulin or the pancreas may not produce enough insulin. Therefore, instead of acting as fuel for the body, glucose builds up in the bloodstream.
Prediabetes risk factors

- Waist size: If you have a large waist size, it could be a sign of insulin resistance. Men with a waist size of more than 40 inches and women with a waist size of more than 35 inches have a higher risk of insulin resistance.
- Weight: obesity or being overweight is one of the main risk factors for prediabetes. Having a large amount of fatty tissue, especially between and inside the skin and muscle around your abdomen, increases the risk of your cells becoming resistant to insulin.
- Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle increases your risk of borderline diabetes. Regular physical activity uses up blood sugar for energy, helps you control your body weight, and makes the cells use insulin more effectively.
- Diet: Eating processed meat, red meat, and consuming sugar-sweetened drinks, is associated with a higher risk of borderline diabetes. A diet high in whole grains, vegetables, fruits, olive oil, and nuts is associated with a significantly lower risk of borderline diabetes.
- Age: Diabetes and prediabetes can occur at any age. However, people aged 45 and lower are at a higher risk of prediabetes.
- Ethnicity or race: Studies show that certain people, including Hispanic, Black, Asian American, and American Indians are at a higher risk of developing prediabetes
- Family History: People who have a sibling or parent with type 2 diabetes are at an increased risk of prediabetes.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome: Women suffering from this condition, which is often characterized by obesity, excessive hair growth, and irregular menstrual cycles, have an increased risk of prediabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: In case you had gestational diabetes (diabetes while pregnant), you and your child have a higher risk of developing prediabetes. If you’ve had diabetes while pregnant, it is extremely important to be screened for prediabetes at least once every two to three years.
- Obstructive sleep apnea: If you suffer from this condition that disrupts normal sleep repeatedly, you have a higher risk of developing insulin resistance.
- Tobacco smoke: Smoking increases your risk of carrying more weight around the belly as well as your risk of developing insulin resistance.
Other conditions commonly associated with borderline diabetes include:
- High levels of triglycerides
- Low levels of good cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein or HDL cholesterol)
- High blood pressure
These conditions are commonly associated with prediabetes, especially when they occur with being overweight or obesity.
The bottom-line
79 million people in the United States have pre-diabetes and many people will develop type two diabetes because of their lack of knowledge. Much of this could be stopped if people knew what to look out for and would talk to their doctor.
Once you have noticed symptoms of prediabetes, you can talk to your doctor and see how to reverse it. A borderline diabetes diet may bring you back to normal levels and keep you from getting type 2 diabetes.
If you have borderline diabetes, the damage of diabetes, especially to your kidneys, heart, and blood vessels, may have already started. Nevertheless, the good news is that progression to type 2 diabetes can be prevented or significantly delayed.
There are two tests that the doctor may give you if diabetes or pre-diabetes is suspected. The fasting glucose test and glucose tolerance test are used to determine if you have prediabetes.
Engaging in regular physical activity, staying at a healthy weight, and eating a healthy diet can help lower your blood sugar level back to within the normal range.





 Symptoms of Early Onset Diabetes
Symptoms of Early Onset Diabetes
 People living with
People living with 


 Childhood diabetes syndrome affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin. Despite being different diseases, both type 1 and type 2 diabetes affect the body’s ability to produce or use insulin. Rates of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are on the rise.
Childhood diabetes syndrome affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin. Despite being different diseases, both type 1 and type 2 diabetes affect the body’s ability to produce or use insulin. Rates of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are on the rise. Don’t miss the symptoms
Don’t miss the symptoms