Diabetic Foot Pain
Are Your Experiencing Diabetic Foot Pain?
Being a diabetic, many parts of the body get damaged, due to having too much glucose in the blood for extended periods. One of the main complaints of diabetics, I’d say would have to be the feet! In a nutshell, the cause of diabetic foot pain is mainly brought about by two main conditions
1. Diabetic Foot Pain & Nerve Damage
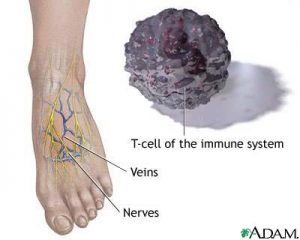
Diabetic neuropathy (damage to the nerves) is a very common complaint that occurs in the legs and feet. Basically, this condition occurs as a result of the normal process of the disease.
This condition can be quite dangerous:
- you may not feel any pain,
- you may not feel hot or cold
- sores, ulcers, and even infection may be present and you’ll never know as you can’t feel it.
How often do we hear the words ‘my feet are killing me’!
Well, those words may well be too true for diabetics, unless good care is taken of your feet and in turn, lessen the diabetic foot pain you are experiencing. There are many home remedies for Diabetic Neuropathy.
Diabetic Foot Pain Treatment
- Start by checking the trend of your blood sugar readings over the past few weeks (has it been a little on the high side). You should ask your Health care professional, his opinion regarding an A1c test. This test determines your levels over a time period. If your blood sugar levels are constantly high, this can contribute to nerve pain.
- A good little gadget is a diabetic foot roller.Just gently massage your feet by running them over the roller. This may help reduce the severity of the pain.
- Massaging the feet with some specialized diabetic foot cream, can play an essential role in preventing some of the problems.
- Make sure you always wear good-fitting, comfortable supportive shoes. You could also invest in some inserts for extra comfort.
2. Diabetic Foot Pain and Poor Circulation.
Diabetes often also brings about poor circulation to the legs and feet. Once again, this is due to high glucose (sugar) levels in the blood, and the effects this has on the arteries, veins and capillaries. Capillaries tend to stiffen and get thicker with extra fatty deposits – this causes problems with delivering correct amounts of oxygen and vital nutrients to the tissues. (Peripheral vascular disease). Veins can swell up, when there becomes more blood they can cope with. Blood then pools into the legs and feet, sometimes even leaking out onto the skin.

I was visiting my Mom recently – she has problems with her feet due to poor blood flow. She bought herself a Circulation Booster and I tell you, the difference for her, was amazing!
How can I help Foot Pain from Poor Circulation?
- It’s a great idea to have a regular check-up with your podiatrist – perhaps once every 6 months.
2. Wear support hose, or get yourself a good pair of ‘diabetic socks’, for when you have long periods of sitting, or when traveling.
3. If you are a smoker, give up! If you are suffering from Peripheral vascular disease (bad circulation) you will definitely benefit from giving up smoking.
4. EXERCISE EXERCISE! Of course, the best way to improve this condition is to make sure you get regular exercise. Walking is great! If you can manage 20-40 minutes a day, 5 days a week, this will make a significant difference to your circulation. A perfect situation is to make sure that you are walking quick enough to puff a little, but not too much so that you have problems holding a conversation.
To sweat just a little is also good. It means your body is working. You will have to make this a life change – a regular part of your daily life from now on. If you’re not quite up to 5 days a week, just start with 2 or 3 and build it up over time.
Once again, massage is great and may also help to reduce diabetic foot pain.












 The basement membrane which is found between the connective and functional tissue is a good example of pericellular matrices. The structure of the basement membrane provides an important anchoring layer that ensures functional cells are kept together. Cells within the extracellular matrix communicate through integrate signals and surface receptors that are associated with their specific function.
The basement membrane which is found between the connective and functional tissue is a good example of pericellular matrices. The structure of the basement membrane provides an important anchoring layer that ensures functional cells are kept together. Cells within the extracellular matrix communicate through integrate signals and surface receptors that are associated with their specific function. Some of the most important constituents of connective tissue, which is mainly composed of the extracellular matrix, are ground substance and fibroblasts. Ground substance is an integration complex between proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, and glycoproteins (mainly fibronectin and laminin). Fibroblasts secrete the matrix constituents in most connective tissues. However, in some specialized connective tissues, like bone and cartilage, matrix components are secreted by osteoblasts and chondroblasts.
Some of the most important constituents of connective tissue, which is mainly composed of the extracellular matrix, are ground substance and fibroblasts. Ground substance is an integration complex between proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, and glycoproteins (mainly fibronectin and laminin). Fibroblasts secrete the matrix constituents in most connective tissues. However, in some specialized connective tissues, like bone and cartilage, matrix components are secreted by osteoblasts and chondroblasts.