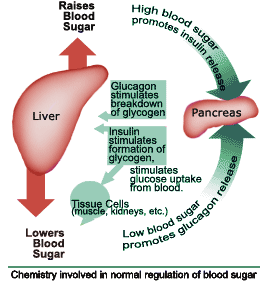
The Normal Fasting Glucose Level
Not long ago, a normal fasting glucose level was never a chief concern for very many people, as the main health worries of the day were heart disease, cancer, and high blood pressure.
Sure there have always been diabetics, but in recent times the number of people diagnosed with diabetes has skyrocketed, even as the number of people diagnosed with heart disease, hypertension, and many forms of cancer have begun to decrease. If the current trend continues, diabetes and diabetes related issues may well become the most important health care concerns of the new millennia. This means that for a growing number of people, having a normal fasting glucose level is more important than ever.
The symptoms to watch for in cases where diabetes may be developing include increased thirst, increased hunger, increased urination, increased fatigue, blurred vision, and lightheadedness. If a person is experiencing two or more of these symptoms it may be time to schedule a test with their physician to determine if they are maintaining a normal fasting glucose level. This is especially true if there is anyone else in their family that has diabetes.
The most common glucose tolerance test is the oral glucose tolerance test, or OGTT. For the OGTT the patient is usually asked to fast for 8 to 10 hours. After the fasting blood glucose level is determined, the patient is given a solution to drink which contains a known quantity of glucose. The blood glucose of the patient is them measured at intervals to determine if their body is correctly metabolizing the glucose which has been ingested. The normal fasting glucose level is usually considered to be between 70 and 99 mg/dl and any reading outside this range may mean that more tests should be run and a possible diagnosis of diabetes.