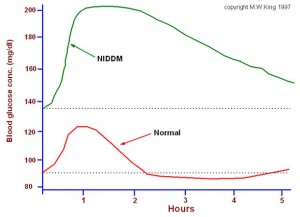
Recognizing Diabetes Symptoms
If you happen to be a diabetic or know someone who is, recognizing what diabetic symptoms are, is very important. This also applies to you if you have a strong family history of diabetes – as you will want to be aware of symptoms if and when you develop the disease too.
Type 2 diabetes usually starts out as a silent disease. Most people with diabetes are unaware they have it. They may dismiss their symptoms –
- fatigue,
- lethargy,
- poor vision,
- irritability,
- reduced libido,
- passing urine more frequently or having to get out of bed at night to go to the toilet – as part of getting older or other problems.
 Symptoms of Early Onset Diabetes
Symptoms of Early Onset Diabetes
Most people who are diagnosed with diabetes have probably already had it for five to ten years. An early symptom of diabetes is that the person may be experiencing episodes of hypoglycemia. With this symptom, the person will suffer tremors, sweating, dizziness, and hunger.
People with symptoms of diabetes-related high blood sugar often have a general feeling of malaise, weight loss, and nausea. You may also feel dizzy or lightheaded. When these symptoms occur, the blood sugar is often above 300 mg/dl, but can be as high as 600 milligrams per deciliter. Glucose greater than 600 milligrams per deciliter can cause an altered sense of consciousness and coma.
People with type I diabetes symptoms are a bit different from diabetes type 2. These guys have some of the symptoms of diabetes type II, but it can get much more serious symptoms such as diabetic ketoacidosis. This occurs when products of metabolism called ketones accumulate in the body. This causes stomach pain, loss of consciousness, and generalized coma, which can be fatal. Type I diabetics may also have symptoms of hypoglycemia if they take too much insulin.

This results in an inability to feel things with their feet. diabetic foot ulcers may develop as a result of poor nerve and circulatory function.
People with diabetes can develop diabetic symptoms of poor visibility. This is because untreated diabetes causes changes in blood vessels of the eyes for vision is poor. The condition is called diabetic retinopathy and can be treated with laser treatments to the retina.
Kidney disease is another symptom of diabetes. This typically occurs when diabetes is not well treated. You may or may not have real symptoms such as fluid retention, but the evidence shows that the kidneys fail. This can lead to the need of a kidney transplant or dialysis if symptoms are severe.
The cardiovascular system may play a role in diabetes. Peripheral vascular disease (or poor circulation in the legs), is a symptom of diabetes. This can lead to cold feet or foot ulcers in diabetics. The heart can also participate. Diabetes is a risk factor for suffering a heart attack.
This is the main reason for the early care of diabetes and control is important for diabetics at all stages of the disease. In fact, most of the complications of diabetes can be improved by early detection.

 Symptoms of Early Onset Diabetes
Symptoms of Early Onset Diabetes
 Although hypoglycemia typically occurs when you’ve not eaten, this is not always the case. Sometimes the symptoms can occur after eating certain foods high in sugar, triggering the body to producing more insulin than needed. This condition is known as postprandial hypoglycemia or reactive hypoglycemia and it can occur in people who have undergone stomach bypass surgery. However, it can also occur in individual who haven’t undergone this surgery.
Although hypoglycemia typically occurs when you’ve not eaten, this is not always the case. Sometimes the symptoms can occur after eating certain foods high in sugar, triggering the body to producing more insulin than needed. This condition is known as postprandial hypoglycemia or reactive hypoglycemia and it can occur in people who have undergone stomach bypass surgery. However, it can also occur in individual who haven’t undergone this surgery.