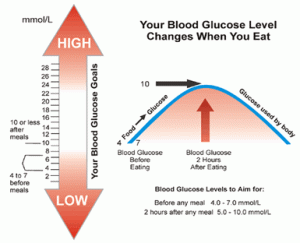
The Importance of a Normal Fasting Blood Glucose
If you or someone you know has a family history of diabetes or has already been diagnosed with diabetes a normal fasting blood glucose is one of the most important things that can be had to control the detrimental health effects of the disease. While glucose is important to the body because every cell in the body uses glucose for fuel, when glucose levels rise to the point where a normal fasting blood glucose cannot be maintained the high glucose levels can begin to damage nearly every body system. Most people are familiar enough with…