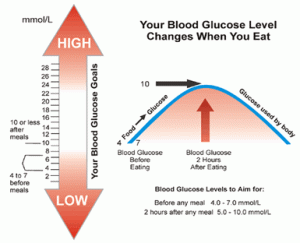
Glucose Level after Eating
The glucose level after eating should be the chief concern of anyone with diabetes, and should be one of the most important tests associated with the disease. In the world of medicine, the things that are considered normal are generally what are to be desired, however, upon close examination of the usual manner of establishing a fasting glucose to determine baseline blood glucose levels there is something decidedly abnormal in the test itself. Normally the fasting blood glucose test is used to diagnose diabetes, but the manner in which the test is administered makes it…