Maintaining the normal glucose level in blood has become more important than ever for a growing number of people. Even as heart disease, stroke, and stroke levels continue to decline the number of people affected by diabetes is rising by leaps and bounds. Diabetes, if not properly treated, can result in kidney failure, heart disease, liver problems, glaucoma, peripheral neuropathy, wounds that won’t heal, and an entire host of other health problems. Though there is, as yet, no cure for diabetes the key to managing the disease and stopping the worst effects is maintaining a normal glucose level in blood.
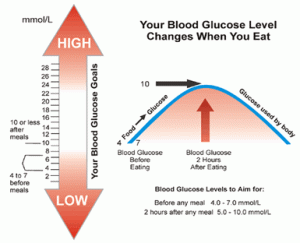
For a healthy individual in normal circumstances the normal glucose level in blood should be somewhere between 60 and 100. This is not a hard and fast rule; however, as the normal glucose level in blood may vary from person to person based on such factors as age, weight, and other health problems. The best way for the individual to determine what the normal glucose level in blood is for them is by visiting their doctor, as the doctor should be able to give the individual good information as to what their normal glucose level in blood should be.
If you have a family history of diabetes and notice that you are experiencing frequent urination, increased appetite, and increased thirst you may be developing diabetes. If you experience any or all of these symptoms for any length of time you should visit your doctor. Your doctor will administer a glucose tolerance test during which you will, after a short period of fasting, be given a glucose solution orally then your blood glucose level will be checked after an appropriate period of time to see if your body is managing glucose correctly. After the test your doctor will be able to tell if the normal glucose level in blood is present and if not get you started with appropriate treatment.
