The amount of sugar (glucose, measured in mg/dL) in the blood fluctuates throughout the day. Blood sugar levels usually depend upon what, how much and when you’ve eaten. Your levels can also change depending on your exercise regimen.
Depending on your treatment plan, your diabetes educator or doctor may recommend checking your blood glucose levels once a week or even up to 10 times a day. Rather than classifying blood sugar levels as being ‘normal’ or abnormal, you can think of them as being “at goal”, “in target” or “in range”.
Although the ADA (American Diabetes Association) provides clear guidelines for blood sugar goals for people living with diabetes, the goals usually vary depending on the time you’re checking your blood glucose.
Normal Blood Sugar:
Fasting normal blood sugar (before eating the first meal)
- Normal fasting blood sugar level (no food for 8 hours) for a person without diabetes: 3.9-5.5 mmol/L (70-99 mg/dL)
- American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommendation for people with diabetes: 4.4-7.2 mmol/L (80-13 mg/dL)
Postprandial (Normal blood sugar two hours after meals)
- Normal for people without diabetes: Lower than 7.8 mmol/L (140 mg/dL)
- American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommendation for people with diabetes: Lower than 10.0mmol/L (180mg/dL)
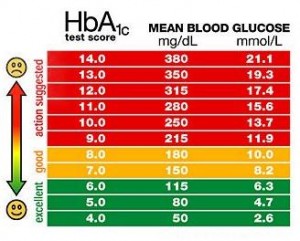
HbA1c
- Normal for people without diabetes: Lower than 5.7%
- American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommendation for people with diabetes: Lower than 7.0%
Blood Glucose Levels and Diabetes
Most people who have been diagnosed with diabetes have wondered at some point what their blood sugar level should be.
Although the responsibility of giving patients the answer to this question rests upon your doctor, physician, nurse practitioner or whoever diagnosed you, not every diabetes patient is given blood glucose goals.
In some cases, you might have been given your glucose goals a long time ago, and they have since been forgotten. However, this shouldn’t be cause for concern – we will discuss all that.
What is blood sugar, anyway?
Blood sugar (or glucose), is glucose that is in the blood. It mainly comes from the food we eat and the main contributors to blood sugar are foods that are rich in carbohydrates, such as fruit, pasta and bread. The cells in your body need sugar for energy in order to perform various functions such as breathing, moving, learning, and thinking. The brain is the body’s command center and it uses about 50% of the energy from blood sugar.
How do things go wrong?
The pancreas is responsible for releasing enzymes and hormones that metabolize food and help the body handle the high glucose levels. Insulin is the main hormone that helps manage blood glucose levels. This is where things can go awry. If your pancreas stops making insulin or doesn’t make enough of it, blood glucose levels can rise too high (type 1 diabetes). Another possible scenario is insulin resistance, where the cells have trouble using insulin properly. This is the main cause of type 2 diabetes.
High blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) can have a wide range of symptoms in the short term, including fatigue, frequent urination and weight loss. If untreated, serious complications can arise, such as ketoacidosis. In the long run (chronic high blood sugar levels), it can lead to more serious complications such as, heart disease, nerve damage, eye disease, as well as disease.
Measuring Blood Glucose Levels
Unless your blood glucose level is too high or too low, you may not always have the signs and symptoms of either low or high blood sugar. In fact, studies show that most people with type 2 diabetes rarely have the symptoms of high blood sugar. As a result, they may go undiagnosed for several years.
One of the best ways to know your blood sugar level is to check it using a glucose meter. The procedure is quite simple and straightforward. It involves doing a finger-stick with a lancet to draw a drop of blood onto the test strip and inserting it into the glucose meter for a reading.
 An alternative way of knowing your blood glucose levels is by using a continuous glucose monitor. The continuous glucose monitor (CGM) reads glucose in the fluid stored between cells (interstitial fluid) approximately every 5 minutes.
An alternative way of knowing your blood glucose levels is by using a continuous glucose monitor. The continuous glucose monitor (CGM) reads glucose in the fluid stored between cells (interstitial fluid) approximately every 5 minutes.
While some doctors are able to provide patients with glucose meters free of charge, continuous glucose monitoring can be expensive, and is not covered by some health plans.

