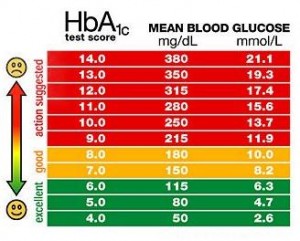
Diabetes Symptoms: Learn to Spot the Symptoms of Diabetes Early
If you listen to your body, you may be able to detect early symptoms of diabetes and are more likely to reverse the disease before it becomes too serious. Remember that diabetes mellitus type 2 is almost always a preventable disease. You may never experience the symptoms of type 2 diabetes – if you are willing and ready to make a firm commitment to a healthy life today!
Types of diabetes:
There are several types of diabetes and most are preventable. Diabetes mellitus type 1 is not definitively known causes and/or treatment. This is also called insulin-dependent diabetes and is characterized by a complete lack of pancreatic function. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, the most common type, usually can be prevented through changes in dietary habits and levels of exercise.
Type 2 diabetes accounts for over 90% of cases of diabetes mellitus.
Gestational diabetes is diabetes that women develop during the later stages of pregnancy. The label is reserved for women who have never before exhibited symptoms of diabetes.
Almost always disappear completely after delivery and ‘very useful during pregnancy – again with healthy eating habits and exercise daily. The symptoms of diabetes:
Please note the following symptoms of diabetes and consult your doctor if you think you are at risk:
- frequent thirst,
- excessive hunger,
- loss weight,
- wounds that heal slowly,
- drowsiness,
- difficulty waking,
- tiredness,
- weakness,
- irritability,
- dry skin and itching,
- velvety skin in the neck or armpits.
What Causes Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus type 2 is caused in most cases by poor food choices, improper diet, and sedentary lifestyle. We need to eat nutritious foods in healthy portions and we have to exercise every day if we want to avoid the development and symptoms of diabetes.
There is simply no other way. Learn new ways of perceiving the same food consumed and physical activity on a new meaning to your life. His day to be much more fun and meaningful reduction in their propensity to develop all diseases – not only diabetes mellitus type 2.
Diabetes research today shows that over 100 million people in the U.S. alone suffer from diabetes or pre-diabetes. These are the people at the highest risk of developing type II diabetes. If you are among them, you need to take immediate action and reassess your habits regarding diet and exercise.
The prevention of type 2 diabetes:
You can prevent diabetes mellitus type 2, with a commitment to positive lifestyle changes like the following:
- start concentrating on eating foods that are mostly water like fruits, vegetables, and legumes,
- eat 5 or 6 small meals on a given day and not just one or two large meals,
- eat your meals at the same time each day,
- remove fast food and processed foods from your life.
Furthermore, no bleached food, microwave food, or fatty foods, avoid excessive alcohol consumption, avoid foods high in sodium, turn and run from trans fats; Drink plenty of water each day, exercise for at least 20 to 30 minutes every day.
Learn how to avoid the development of symptoms of diabetes today and commit to a healthy lifestyle! You and your loved ones will be much happier for it.



 Symptoms of Early Onset Diabetes
Symptoms of Early Onset Diabetes