Understanding the Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia refers to a condition caused by low blood glucose levels. Glucose is the body’s main source of energy and a hormone known as insulin aids cells in absorbing and using glucose.
Hypoglycemia typically occurs with several conditions but is most commonly associated with diabetes medications, such as insulin. It is particularly common in individuals with diabetes who also have issues with food, medication, or exercise. However, other drugs and conditions can also cause low levels of blood sugar in people without diabetes. There are two types of non-diabetic hypoglycemia:
- Fasting hypoglycemia, which can be linked to a disease or some medications
- Reactive hypoglycemia, which typically occurs a few hours after eating a meal
What are the Symptoms of Hypoglycemia?
For most people, the symptoms of hypoglycemia usually appear when their blood glucose is 70 mg/dL (milligram per deciliter) or lower. However, this number might vary between individuals and the symptoms can also be different. Common signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia include:
- Anxiety
- Shakiness
- Pale skin
- Hunger
- Sleepiness
- Irritability
- Numbness of the cheeks, lips or tongue
- Irregular or fast heartbeat
- Sweating
- Crankiness
- Dizziness
As the blood sugar level goes lower, symptoms can include:
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness, passing out
- Seizures
- Blurred vision
Causes of hypoglycemia
Possible causes in people with diabetes
People with diabetes might not be responsive to insulin (type 2 diabetes) or they might not make enough of it (type 1 diabetes). This causes glucose to accumulate in the blood stream to high levels. Therefore, most people with diabetes take medications such as insulin to correct this problem by lowering blood sugar levels.
However, too much insulin may cause blood glucose levels to drop to extremely low levels, causing hypoglycemia. Other factors that can cause hypoglycemia include eating less than you normally do especially after taking diabetes drugs, or exercising more than usual.
Possible causes in people without diabetes
Causes of hypoglycemia in people without diabetes include:
- Excessive alcohol consumption: Heavy drinking without eating blocks the liver from releasing glucose, causing hypoglycemia.
- Medications: Taking oral diabetes medication without a prescription is one of the possible causes of hypoglycemia. Various medications, such as quinine can also cause hypoglycemia in people with kidney failure or in children.
- Long-term starvation: Eating disorders, such as anorexia nervosa, might result in low blood glucose levels.
- Some illnesses: Liver illnesses such as severe cirrhosis or hepatitis can cause low blood glucose levels and ultimately hypoglycemia. Some severe kidney illnesses can also cause hypoglycemia by keeping the body from excreting medications and causing a buildup of medications which can affect glucose levels.
- Hormone deficiencies: Some pituitary tumor and adrenal gland disorders can cause a deficiency of hormones that are responsible for regulating glucose production. In children, hypoglycemia can occur if they have extremely low levels of growth hormone.
- Insulin overproduction: Insulinoma (tumor of the pancreas) can cause excessive insulin release, which can result in hypoglycemia. Various other tumors can also result in overproduction of insulin-like substances in the body. Enlargement of pancreas cells can cause overproduction of insulin, causing hypoglycemia.
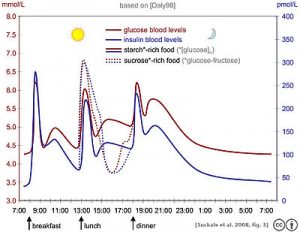
Hypoglycemia after meals

Hypoglycemia Complications
If untreated, hypoglycemia can lead to:
- Weakness and dizziness
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizure
- Injuries
- Falls
- Motor vehicle accidents
- Greater risk of dementia particularly in older adults
- Death
What is Hypoglycemia Unawareness
Recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia can cause hypoglycemia unawareness, a condition whereby the body no longer produces symptoms that warn of low blood sugar level, such as irregular heartbeats and shakiness. As a result, the risk of severe hypoglycemia increases.
For people with diabetes and hypoglycemia unawareness, their doctors might recommend blood sugar awareness training, raise their blood sugar level goals and modify treatment.
Under treated Diabetes
For people with diabetes episodes of hypoglycemia can be frightening and uncomfortable. This fear can cause them to modify their treatment without consulting a physician, which can cause uncontrolled diabetes. Hypoglycemia can be a life-threatening condition. Moreover, you should not change your medication dose without consulting your doctor.
Therefore, it’s extremely important to seek medical attention if you experience the symptoms of hypoglycemia or if hypoglycemia is not responding to treatment, whether you have diabetes or not.


 which can be life threatening in the end. Extremely high blood sugar symptoms include tiredness, dehydration, a very dry mouth, vomiting and nausea, excessive urination, stomach pain and other side effects. Hypoglycemia, or extremely low blood sugar, is also very dangerous and can lead to fainting, dizziness, confusion, hunger, feeling sweaty or clammy, increased heartbeat and other serious life threatening problems that can be dealt with by adding some simple sugar to the system.
which can be life threatening in the end. Extremely high blood sugar symptoms include tiredness, dehydration, a very dry mouth, vomiting and nausea, excessive urination, stomach pain and other side effects. Hypoglycemia, or extremely low blood sugar, is also very dangerous and can lead to fainting, dizziness, confusion, hunger, feeling sweaty or clammy, increased heartbeat and other serious life threatening problems that can be dealt with by adding some simple sugar to the system.




