Signs and Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
An Overview of the Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) is a condition that typically occurs when the amount of glucose in the blood is too high. Although hyperglycemia usually affects diabetics, it can also occur in people without diabetes or other underlying conditions.
Some of the main factors that can cause hyperglycemia in people with diabetes include illness, changes in physical activity and diet, not taking enough or skipping glucose-lowering drugs, or non-diabetes medication. Hyperglycemia needs immediate medical attention because if uncontrolled, it can easily lead to a wide range of life-threatening complications, including diabetes coma and complications affecting your kidneys, heart, nerves, and eyes.
There are two main kinds of hyperglycemia:
- After-meal (Postprandial) hyperglycemia where the blood glucose is greater than 180 mg/dL two hours after eating.
- Fasting hyperglycemia where the blood sugar is greater than 130 mg/dL after not drinking or eating for at least eight hours.
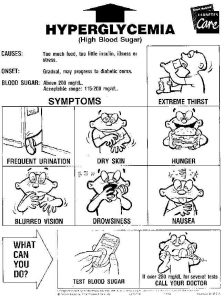
Symptoms of hyperglycemia
Most people rarely notice any hyperglycemia symptoms until their blood sugar levels are significantly elevated – typically to levels above 180 mg/dL or 10 mmol/L. Hyperglycemia symptoms usually develop gradually over several days or even weeks and symptoms become worse the longer blood glucose levels stay high. However, it’s essential to keep in mind that some people who have type 2 diabetes for extended periods of time may not experience any symptoms despite having elevated blood glucose levels.
Early signs of hyperglycemia
It is essential to identify the early signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia in order to seek prompt medical attention. Some of the early signs and symptoms include:
- Headache
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Increased thirst
- Blurred vision
Later Signs of hyperglycemia
- Trouble concentrating
- Weight loss
- Tingling or numbness in the feet
- Blood glucose level higher than 180mg/dL
If untreated, hyperglycemia can lead to the buildup of ketones (toxic acids) in the urine and blood (ketoacidosis). Later signs and symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Confusion
- Dry mouth
- Fruity-smelling breath
- Abdominal pain
- General weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Coma
Untreated hyperglycemia can cause other serious complications such as:
- Impaired vision
- Skin and vaginal infections
- Slow-healing sores and cuts
- Damage to the kidneys, blood vessels, and eyes
- Intestinal problems including diarrhea and chronic constipation
- Nerve damage leading to insensitive, cold, or painful feet, erectile dysfunction, or loss of hair.
Causes of Hyperglycemia
During digestion, our bodies break down carbs from food – such as pasta, rice, and bread – into sugar molecules such as glucose. Glucose is normally absorbed directly into the bloodstream after eating; however, it requires insulin’s assistance to be absorbed by cells in tissues.
When your blood glucose level is high, the pancreas is stimulated to release insulin which is essential for the optimum functioning of cells.
Extra glucose is usually stored in the muscles and liver as glycogen. Due to this process, the amount of glucose in the bloodstream is lowered hence preventing it from rising to dangerously high levels.
Conditions such as diabetes lower the effects of insulin on the body. Consequently, glucose builds up in the bloodstream and may reach high levels (hyperglycemia) if left untreated.
Risk factors
Some of the factors that can contribute to dangerously high blood sugar levels include:
- Being inactive
- Not using prescribed medication such as insulin
- Having an infection or illness
- Use of certain medications, including steroids
- Using expired insulin
- Having surgery or being injured
- Emotional stress
When should you see your doctor?
- Seek medical assistance immediate medical attention if:
- Your blood sugar levels are consistently above 13.3 mmol/L (240 mg/dL) and you have toxic acids (ketones) in your urine
- You’re sick and are unable to keep any fluids or food down
- You’re experiencing ongoing vomiting or diarrhea, but you are able to tolerate some drinks or foods
- You have a persistent fever
- You’re having trouble keeping your blood sugar levels within the recommended range
Maintaining your blood glucose levels within the recommended range plays a major role in preventing most diabetes-related complications such as kidney damage (diabetic neuropathy), cardiovascular disease, neuropathy (nerve damage), kidney failure, joint and bone problems, gum and teeth infections, and cataracts.